Fortran
这个语言简直伤天害理,但确是笔者前老板最爱的语言,而且是f77,天灭fortran。可超算比赛 fortran 的上镜次数还挺多的,之前做天气应用的时候没敢改,现在既然有个小于 15w 行的程序,笔者尝试着修改。
PGI 编译器是一个商用编译器。后被 NV 收购,加了很多 fortran 可用的 cuda DSL。这无疑让 fortran 续命了不少。NVHPC 中的 Nvfortran 有很多编译器优化的 log 可以看。
基本语法: module 相当于 c 中的struct。 program(main)/function(normal function) 相当于 对function 的定义
real function square(x)
implicit none
real, intent(in) :: x
square = x * x
return
end function square
program main
integer :: n, i, errs, argcount
real, dimension(:), allocatable :: a, b, r, e
n = 1000000
call square(n)
end program
subroutine 相当于trait,需要有generic function 来实现
OpenACC
一个简单的加法
module mpoint
type point
real :: x, y, z
end type
type(point) :: base(1000)
end module
subroutine vecaddgpu( r, n )
use mpoint
type(point) :: r(:)
integer :: n
!$acc parallel loop present(base) copyout(r(:))
do i = 1, n
r(i)%x = base(i)%x
r(i)%y = sqrt( base(i)%y*base(i)%y + base(i)%z*base(i)%z )
r(i)%z = 0
enddo
end subroutine
Mind to use Makefile to see the Optimization info from the compiler. Also checkt the identifier loop present and copyout specify the gpu to run on.
nvfortran -MInfo -Mbounds
During the runtime, you can see the symbol and source file and using which GPU.
NVCOMPILER_ACC_NOTIFY=1 /root/yyw/cmake-openacc/cmake-build-debug-nvhpc/acc_test
Let's compared with the Kernel version. Both option -O0 -g
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
__global__ void vecaddgpu(int **a, int **b, int **c, int i) {
*c[i] = *a[i] + *b[i];
}
int main(void) {
int n = 1000000000;
int *a = static_cast<int *>(malloc(n * sizeof(int)));
int *b = static_cast<int *>(malloc(n * sizeof(int)));
int *c = static_cast<int *>(malloc(n * sizeof(int))); // host copies of a, b, c
int *e = static_cast<int *>(malloc(n * sizeof(int))); // result
int **d_a, **d_b, **d_c; // device copies of a, b, c
int size = sizeof(int);
int err = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = i;
b[i] = 1000 * i;
e[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
// Allocate space for device copies of a, b, c
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_a, size * n);
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_b, size * n);
cudaMalloc((void **) &d_c, size * n);
// Copy inputs to device
cudaMemcpy(d_a, reinterpret_cast<const void *>(a), size * n, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_b, reinterpret_cast<const void *>(b), size * n, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Launch vecaddgpu() kernel on GPU with N blocks
vecaddgpu<<<1, 1024>>>(d_a, d_b, d_c, n);
// Copy result back to host
cudaMemcpy(c, d_c, size * n, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Cleanup
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (c[i] != e[i])
err++;
}
free(a);
free(b);
free(c);
cudaFree(d_a);
cudaFree(d_b);
cudaFree(d_c);
return 0;
}
效率对比
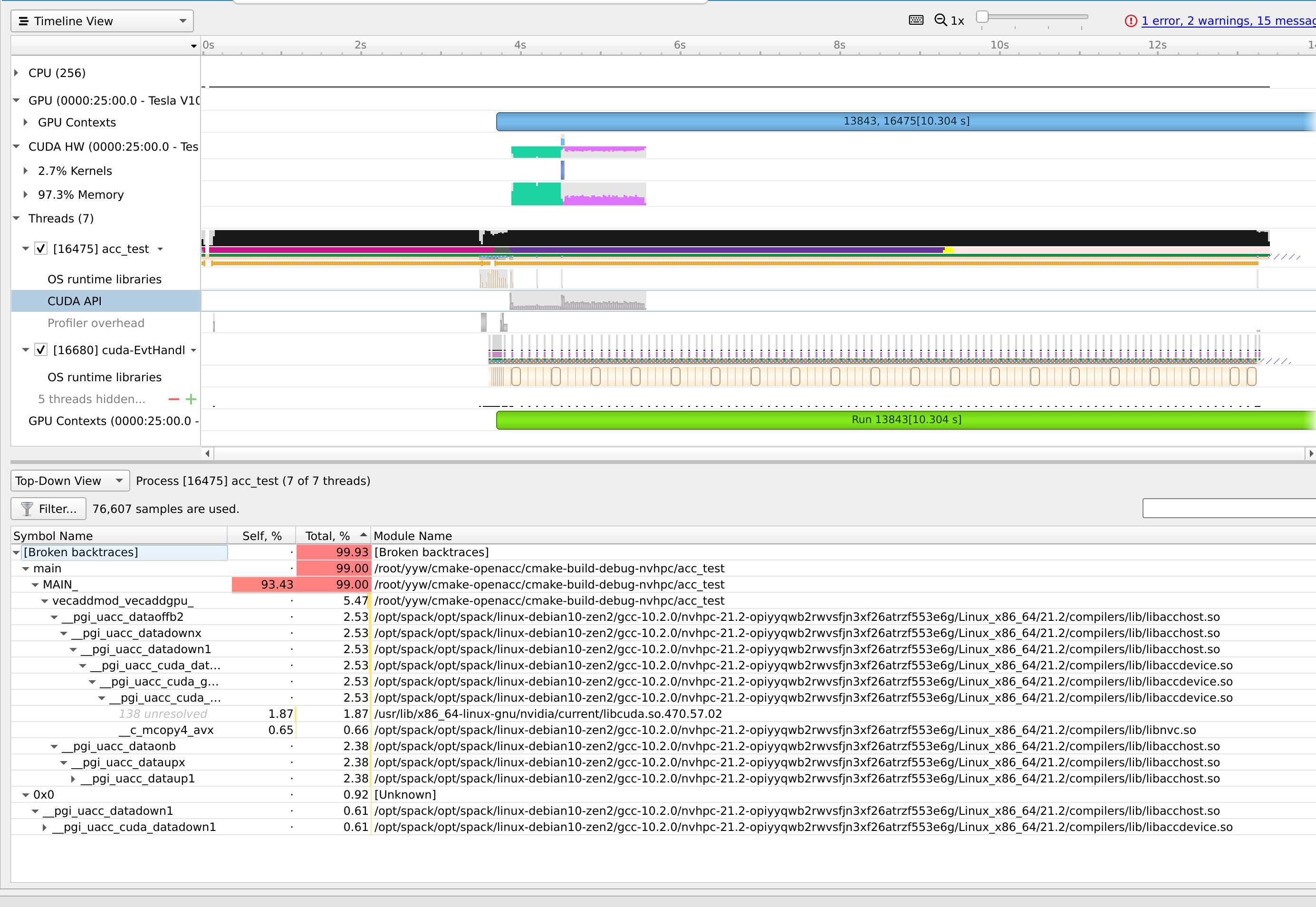
pure cuda kernel is 1.5x faster.